OVERVIEW
We’re very excited to have you in class this semester! Our aim is to make this course as inclusive, diversified, and open as possible, and we will offer an undergraduate and graduate version of the course:
- 6.8611: Undergraduate version (CI-M component required)
- 6.8610: Graduate version (no CI-M option)
Note: all Harvard students who wish to take the course must enroll in 6.8610.
DESCRIPTION
How can computers understand and leverage text data and human language? Natural language processing (NLP) addresses this question, and in this course students study both modern and classic approaches. We will mainly focus on statistical approaches to NLP, wherein we learn a probabilistic model based on natural language data. This course provides students with a foundation of advanced concepts and requires students to conduct a significant research project on an NLP problem of their choosing, culminating with a high-quality paper (5-8 pages). Assessment also includes (3) homework assignments, special topic responses, and a midterm exam. Our goal is to help challenge each student to elicit one’s best, and along the way for the course to be one of your most fun and rewarding educational experiences.
STAFF
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Jacob Andreas (Instructor) | Chris Tanner (Instructor) | Thomas Pickering (WRAP) | Michael Maune (WRAP) | Taylor Braun (Course Assistant) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Angela Li (TA) | Baile 'Peter' Chen (TA) | Chaitanya Ravuri (TA) | Daniel Li (TA) | Gabriel Grand (TA) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Hassan Mohiuddin (TA) | Heidi Lei (TA) | Michael Hadjiivanov (TA) | Nicholas Tsao (TA) | Philip Schroeder (TA) |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Puja Balaji (TA) | Ryan Welch (TA) | Sarah Zhang (TA) |
LOGISTICS
LECTURE
- Tuesdays and Thursdays @ 11am - 12:30pm in 32.123 (may change locations, depending on enrollment)
- Lectures are in-person
- Attendance and active participation is highly encouraged to facilitate an enriching learning environment for everyone
OFFICE HOURS
- Monday 4:00 - 5:30 - Room 32-144
- TA Staff: Puja, Angela
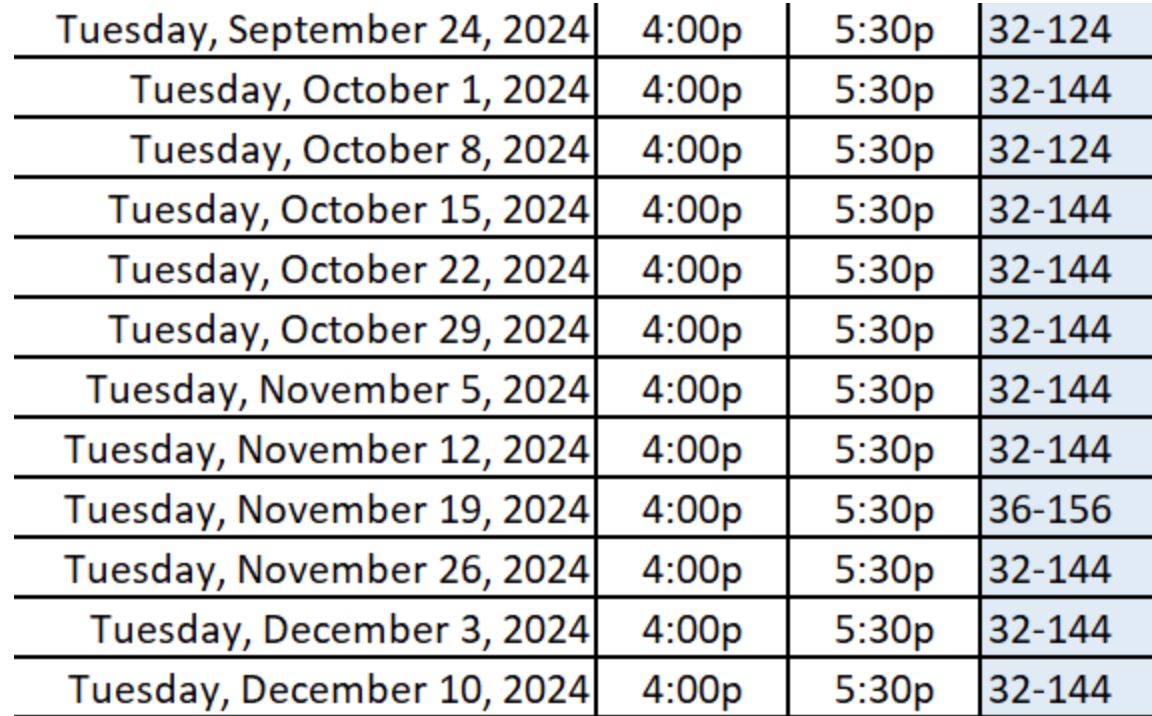
- Tuesday 4:00 - 5:30 - Room 32-144* (except 9/24, 10/8, 11/19) or on Zoom (link on Canvas)
- TA Staff: Gabe, Heidi, Peter, (Sarah on Zoom)
- Wednesday 4:00 - 5:30 - Room 32-144
- TA Staff: Philip, Chaitanya, Hassan, Michael
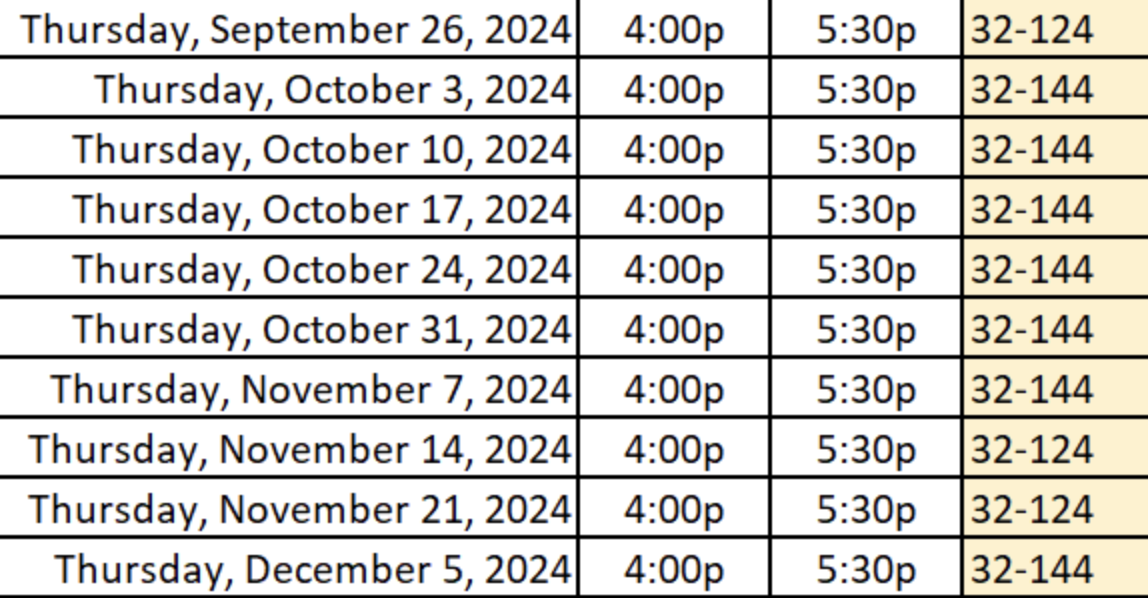
- Thursday 4:00 - 5:30 - Room 32-144* (except 9/26, 11/14, 11/21)
- TA Staff: Daniel, Ryan, Nicholas
*some exceptions apply to Tuesdays/Thursday OH locations, please check the following graphics:
 |
 |
GRADING
- Foundation: Midterm exam: 20% (Oct 29)
- Foundation & Application: Homework assignments: 30% (3 HWs, roughly two weeks for each)
- Guest Lectures: Special topic responses: 5%
- Creating New Knowledge: Research Project: 45% (twelve weeks)
ENROLLMENT
The demand for this course content is extremely high, and we’re thrilled to see so many curious students! Over 400 students have registered for the course, so we are resource-constrained. To provide as smooth of an educational experience as possible, we strongly recommend that every enrolled student has a strong foundation in Machine Learning, and we will enforce having the sufficient pre-req courses.
PREREQUISITES
No prior NLP experience is expected or necessary, but students must have a basic foundation in probability and calculus, along with strong knowledge of Machine Learning. See the syllabus for more details, along with HW #0 (ungraded) to assess if your current knowledge is aligned with the pre-req expectations – you should be able to answer all of the questions without too much difficulty.
WHAT’S NEW?
NLP is an incredibly fast-moving field! Fun fact, ChatGPT was released the day before our final lecture of the semester in Fall 2022. Since then, NLP and GenerativeAI has become a household name. To showcase recent progress within NLP, we are introducing approximately three new lectures that span topics including: decoding (search and sampling), mixture-of-experts (MoE), quantization of transformers, state-space models such as Mamba. We’ll also have a new guest lecture with insights about training LLMs in industry! Consequently, to make room for such, we are removing some of our content about structured predictions. e.g., Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and Conditional Random Fields (CRFs).
NOTE: Despite the immense capabilities of large language models (LLMs), this course will be strongly rooted in providing a foundation for NLP; that is, we will cover a wide range of modelling approaches that include LLMs and more.
QUICK ACCESS
- Canvas: homework assignments and course announcements
- Project Ideas (coming soon): on-going spreadsheet to collaboratively find and create research projects
- Emergency Helpline: for private concerns, issues, and questions (not course content)
- Supplemental Resources: a compilation of useful, external resources
